|
Source:
Mexico and the United States.
2002
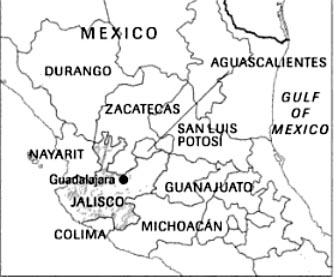
Jalisco has a land surface of 30,000 square miles (80,000 sq. km).
Its geography varies from flat coastline on the Pacific Ocean to the
high Sierra Madre Occidental mountain range to the north.
The state of Jalisco is located in
western Mexico and borders the states of Durango, Zacatecas,
Aguascalientes, Nayarit, Guanajuato, San Louis Potosi, Michoacán,
and Colima. It is famous as the center of Mexico's information
technology industry.
The name Jalisco derives from the Nahuatl words
xalli, meaning sand or gravel, and ixili, meaning plain."
In 2000 it had a population of nearly six million, about 6.5 percent
of Mexico's total population. With its 215-mile (ert-km)
coastline it is known for its resorts, including the renowned Puerto
Vallarta. The state's capital is Guadalajara, which is
Mexico's second largest city.
Jalisco has a varied climite because of its geography.
It is dominated by the southern end of the Siera Madre Occidental
and the western end of the chain of volcanic mountains traversing
central Mexico. Its landscape ranges form fresh pine woods to
tropical forest. The country's largest lake, Lake Chapala, is
in the center of hte state. Jalisco has a semitropical
climate; temperatures are ware for most of hte year but hot and
humid in July and August. The rainy season is from June to
October.
History.
The Spanish invaded what was to become
Jalisco in 1529, when conquistador Nuno de Guzman began an incursion
into the area. The region was later included in New Galicia.
In 1823 Jalisco was declared a state; at the time it also included
areas that now form part of the states of Nayarit, Colima, and
Zacatecas. In the war against the United States (1846-1848)
Jalisco contributed troops that took part in conflicts in Angostura,
Nuevo Leon, and Palo Alto. Shortly before the War of Reform
(1858-1861) Jalisco became a leading state in the liberal revolution
led by Benito Juárez
(1806-1872). Jalisco was occupied by the French during the
Wars of Intervention but was recaptured in 1866, and in 1884 Nayarit
state was separated from Jalisco. In the years after the
Mexican Revolution (1910-1920) the Cristero Rebellion enjoyed its
strongest support in the state.
Economy
Agriculture and livestock breeding are
two of the most important economic activities in Jalisco. The
state is now Mexico's leading producer of corn, milk, sugar, and
poultry. Other crops grown include beans, oats, chile,
alfalfa, and onions. Jalisco produces internationally renowned
handicrafts, including typical products made of brown glass, wrought
iron, papier-mâché,
and leatherwork. The production of tequila is important in the
Los Altos region of hte state, which is often referred to as "the
most Mexican" state because, in addition to tequila, it is the
presumed birthplace of mariachi music. Fishing and tourism are
key activities on the coast.
In recent years Jalisco has become known as the Silicon
Valley of Mexico because many U. S. Electronics firms, taking
advantage of the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), have
established operations there. The main electronic products
manufactured are computers, cellular phones, and printers. The
state's exports are now worth more than U. S. $3 billion annually.
Joanna Griffin
SEE ALSO:
Agriculture; Crafts; Guadalajara; Manufacturing; Mariachis; NAFTA;
Tourism.
|